Balancing equations lab answer key – Embark on a journey to decipher the intricacies of balancing equations with our comprehensive lab answer key. This guide unveils the secrets behind chemical reactions, empowering you with the knowledge to navigate the complexities of stoichiometry and predict the outcomes of chemical transformations.
Delve into the fundamentals of balancing equations, unraveling the steps involved and exploring the different types of chemical reactions. Discover the significance of stoichiometry in understanding the quantitative relationships between reactants and products. Witness the practical applications of balancing equations in diverse fields, from chemistry and engineering to medicine.
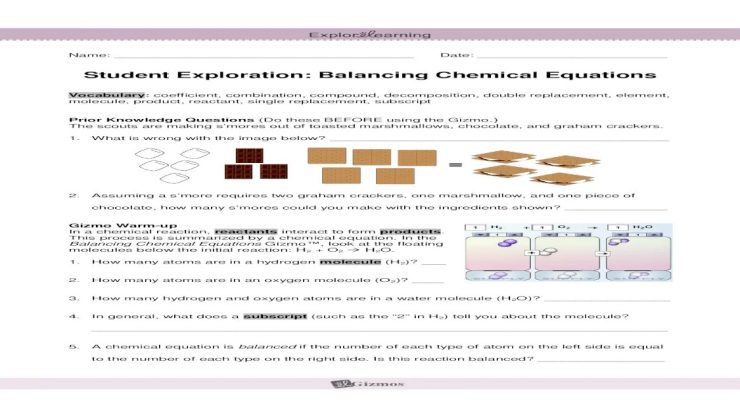
Balancing Equations Lab: Balancing Equations Lab Answer Key
The purpose of balancing chemical equations is to ensure that the number of atoms of each element is the same on both sides of the equation. This is important because chemical reactions must obey the law of conservation of mass, which states that matter cannot be created or destroyed.
To balance a chemical equation, the following steps can be taken:
- Write the unbalanced equation.
- Identify the atoms that are not balanced.
- Add coefficients to the reactants and products to balance the atoms.
- Check to make sure that the equation is balanced.
For example, the following unbalanced equation can be balanced by adding a coefficient of 2 to the hydrogen gas reactant:
“`
H2 + O2 → 2H2O
“`
Types of Chemical Reactions
There are four main types of chemical reactions:
- Synthesis reactions
- Decomposition reactions
- Single displacement reactions
- Double displacement reactions
In a synthesis reaction, two or more reactants combine to form a single product. For example:
“`
H2 + O2 → 2H2O
“`
In a decomposition reaction, a single reactant breaks down into two or more products. For example:
“`
H2O → 2H2 + O2
“`
In a single displacement reaction, one element replaces another element in a compound. For example:
“`Fe + 2HCl → FeCl2 + H2“`
In a double displacement reaction, two compounds exchange ions to form two new compounds. For example:
“`NaCl + AgNO3 → AgCl + NaNO3“`
Stoichiometry
Stoichiometry is the study of the quantitative relationships between reactants and products in chemical reactions. It is used to calculate the amount of reactants and products that are needed or produced in a reaction.
The mole ratio of reactants and products in a balanced chemical equation can be used to calculate the amount of each substance that is needed or produced. For example, the mole ratio of hydrogen gas to oxygen gas in the following reaction is 2:1:
“`
H2 + O2 → 2H2O
“`
This means that for every 2 moles of hydrogen gas that react, 1 mole of oxygen gas is needed. Similarly, for every 2 moles of hydrogen gas that react, 2 moles of water are produced.
The limiting reactant in a chemical reaction is the reactant that is completely consumed in the reaction. The limiting reactant determines the amount of product that can be produced.
Applications of Balancing Chemical Equations
Balancing chemical equations is a fundamental skill in chemistry. It is used in a variety of applications, including:
- Predicting the products and quantities of chemical reactions
- Designing chemical processes
- Understanding the stoichiometry of chemical reactions
- Solving stoichiometry problems
Balancing chemical equations is also used in a variety of other fields, such as engineering and medicine. For example, engineers use balanced chemical equations to design chemical processes, and doctors use balanced chemical equations to understand the metabolism of drugs.
FAQ Compilation
What is the purpose of balancing chemical equations?
Balancing chemical equations ensures that the number of atoms of each element on the reactants’ side of the equation equals the number of atoms of that element on the products’ side, adhering to the law of conservation of mass.
How do I balance a chemical equation?
Balancing chemical equations involves adjusting the stoichiometric coefficients in front of each chemical formula until the number of atoms of each element is identical on both sides of the equation.
What is stoichiometry used for?
Stoichiometry enables the calculation of the quantitative relationships between reactants and products in a balanced chemical equation, allowing for the prediction of reaction outcomes and the determination of limiting reactants.