Cells of the immune system student worksheet – Welcome to the definitive resource on cells of the immune system, a student worksheet that delves into the intricate workings of our body’s defense mechanism. This comprehensive guide unravels the mysteries of the immune system, providing a clear and engaging overview of its components, functions, and interactions.
As we embark on this educational journey, we will explore the diverse cells that orchestrate our immune response, from the sentinels of the innate system to the adaptive soldiers that mount targeted attacks against pathogens. Through detailed descriptions and insightful explanations, this worksheet empowers students with a profound understanding of the immune system’s vital role in safeguarding our health.
Immune System Overview
The immune system is a complex network of cells, tissues, and organs that protects the body from infections and other threats. Its primary functions include:
- Recognizing and eliminating foreign invaders, such as bacteria, viruses, and parasites
- Distinguishing between self and non-self, preventing autoimmune disorders
- Maintaining immune tolerance, preventing allergic reactions and other hypersensitivity responses
The immune system has two main branches:
- Innate immune system: Provides immediate, non-specific defense against pathogens
- Adaptive immune system: Develops specific responses to specific pathogens, providing long-term immunity
Cells of the Immune System
| Cell Type | Function | Innate or Adaptive | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Neutrophils | Phagocytosis of bacteria and fungi | Innate | – |
| Macrophages | Phagocytosis of larger particles, antigen presentation | Innate | – |
| Natural killer cells | Killing of infected or cancerous cells | Innate | – |
| B cells | Antibody production | Adaptive | – |
| T cells | Cell-mediated immunity, killing of infected cells | Adaptive | – |
| Antigen-presenting cells | Display of antigens to T cells | Innate and Adaptive | Dendritic cells, macrophages |
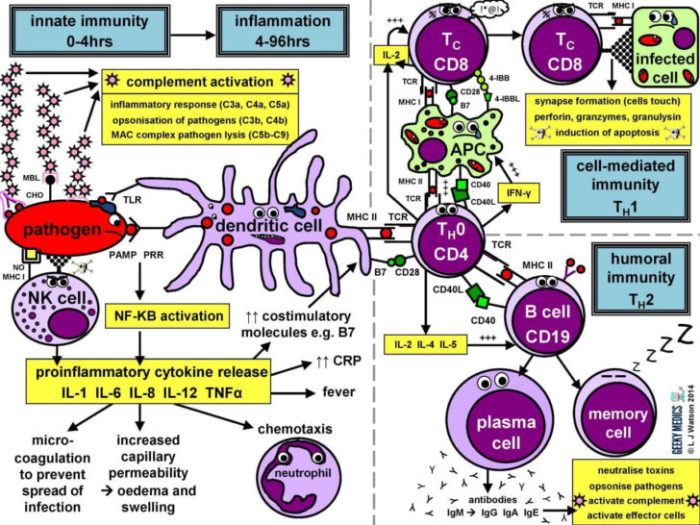
Innate Immune Response
The innate immune response is the first line of defense against pathogens. It involves:
- Physical barriers: Skin, mucous membranes, and cilia
- Chemical mediators: Interferons, cytokines, and complement proteins
- Phagocytosis: Engulfing and destroying foreign particles by cells such as neutrophils and macrophages
Adaptive Immune Response
The adaptive immune response is a highly specific and long-lasting defense mechanism. It involves:
- Antigen presentation: Display of antigens by antigen-presenting cells to T cells
- Antibody production: Production of antibodies by B cells to neutralize pathogens
- Cell-mediated immunity: Killing of infected cells by T cells
Interactions between Immune Cells

Immune cells interact with each other through cell-cell signaling and cytokine production. These interactions contribute to the coordinated immune response. For example:
- Neutrophils release cytokines that attract macrophages to the site of infection
- T cells activate B cells to produce antibodies
- Antigen-presenting cells display antigens to T cells, initiating the adaptive immune response
Immune Disorders: Cells Of The Immune System Student Worksheet
Immune disorders occur when the immune system malfunctions. Common disorders include:
- Allergies: Hypersensitivity reactions to specific allergens
- Autoimmune diseases: Immune system attacks the body’s own tissues
- Immunodeficiency disorders: Weakened immune system, leading to increased susceptibility to infections
Immune System in Health and Disease
The immune system plays a crucial role in maintaining overall health. It protects the body from infections, prevents cancer development, and helps repair damaged tissues. Lifestyle factors, such as diet, exercise, and stress, can influence immune function.
Expert Answers
What is the primary function of the immune system?
To protect the body from pathogens, such as bacteria, viruses, and parasites.
What are the two main branches of the immune system?
Innate immunity and adaptive immunity.
What is the role of neutrophils in the innate immune response?
To engulf and destroy pathogens through phagocytosis.
What is the function of T cells in the adaptive immune response?
To recognize and destroy specific pathogens.

