Electron Dot Formulas and Shape Lab 9 embarks on a captivating exploration into the fascinating world of molecular structures, unraveling the intricate relationship between electron configurations and geometric arrangements. Delving into the fundamental principles of chemistry, this lab unveils the secrets of electron dot formulas, providing a powerful tool for understanding and predicting the behavior of atoms and molecules.
Through engaging demonstrations and interactive exercises, Electron Dot Formulas and Shape Lab 9 empowers students to visualize and comprehend the electronic structures of various elements and compounds. By examining the distribution of valence electrons, learners gain insights into the formation of chemical bonds, the prediction of molecular shapes, and the reactivity of substances.
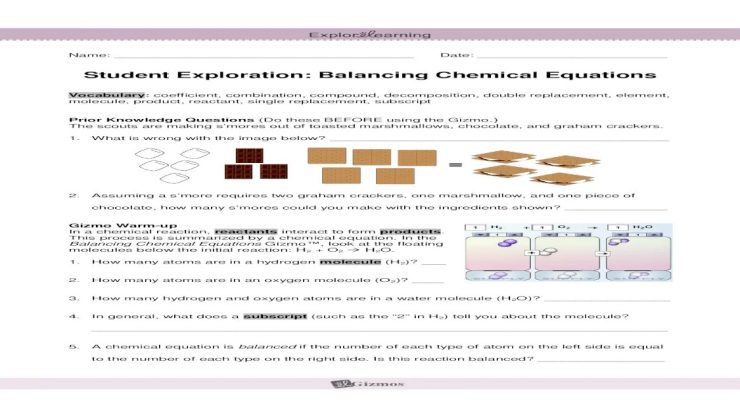
1. Introduction to Electron Dot Formulas

Electron dot formulas, also known as Lewis dot structures, are a graphical representation of the valence electrons in an atom or molecule. They provide a simplified way to understand the chemical bonding and electronic structure of substances.
Valence electrons are the electrons in the outermost energy level of an atom, and they play a crucial role in determining the chemical properties of the element. The number of dots in an electron dot formula represents the number of valence electrons.
Examples of Electron Dot Formulas
- Hydrogen: H:
- Helium: He:
- Carbon: :C:
- Nitrogen: :N:
- Oxygen: :O:
2. Predicting Molecular Shapes Using Electron Dot Formulas
The electron dot formula of a molecule can be used to predict its molecular shape. The VSEPR (Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion) theory states that electron pairs in the valence shell of an atom will repel each other, resulting in a molecular shape that minimizes this repulsion.
Examples of Molecular Shapes
- Linear (2 electron pairs): BeCl 2
- Trigonal planar (3 electron pairs): BF 3
- Tetrahedral (4 electron pairs): CH 4
- Trigonal pyramidal (3 electron pairs and 1 lone pair): NH 3
3. Electron Dot Formulas and Chemical Bonding
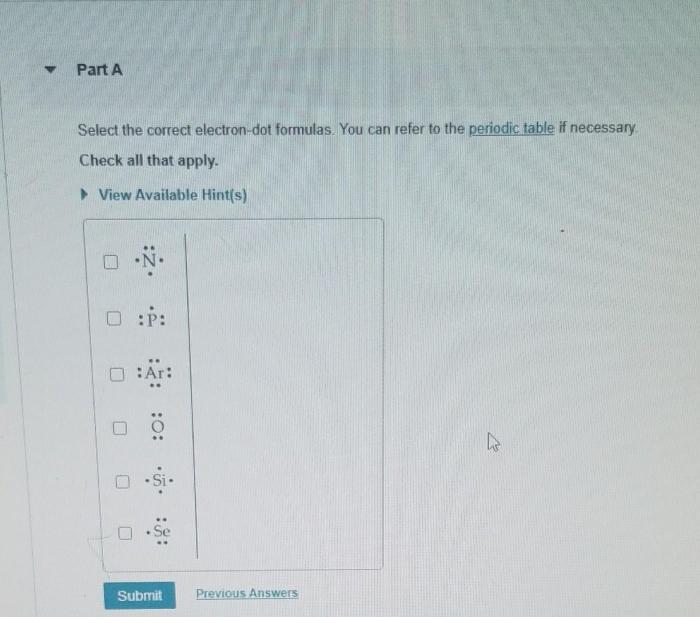
Electron dot formulas can be used to represent different types of chemical bonds between atoms.
Types of Chemical Bonds, Electron dot formulas and shape lab 9
- Covalent bond: A bond formed when two atoms share one or more pairs of electrons.
- Ionic bond: A bond formed when one atom transfers one or more electrons to another atom, creating oppositely charged ions.
- Metallic bond: A bond formed between metal atoms, where the valence electrons are delocalized throughout the metal lattice.
4. Applications of Electron Dot Formulas
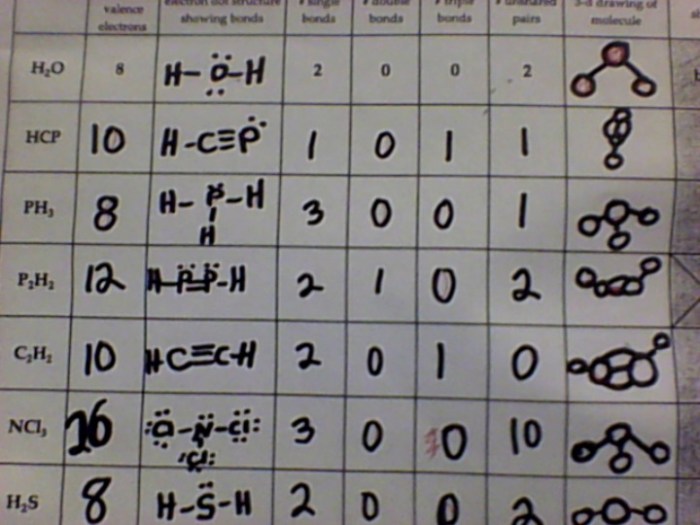
Electron dot formulas have numerous practical applications in chemistry, including:
Applications
- Predicting the reactivity of molecules
- Understanding the electronic structure of materials
- Designing new drugs and materials
Top FAQs: Electron Dot Formulas And Shape Lab 9
What are electron dot formulas?
Electron dot formulas are symbolic representations of atoms and molecules that depict the arrangement of valence electrons around the atomic nuclei.
How do electron dot formulas help predict molecular shapes?
Electron dot formulas provide insights into the number of electron pairs surrounding an atom, which, according to VSEPR theory, determines the molecular geometry and shape.
What is the significance of valence electrons in electron dot formulas?
Valence electrons are the electrons in the outermost energy level of an atom, and their number determines the number of dots or lines used to represent the electron pairs in an electron dot formula.